# Built in stack data structure in C++
Stack is a data structure which follows LIFO i.e. Last-In-First-Out method.
The data/element which is stored last in the stack i.e. the element at top will be accessed first.
Both insertion & deletion takes place at the top.
To use stack in C++ we have to include teh header file
#include <stack>and then we can define stack of any type using the formatstack <TYPE> name;for example :stack <int> s1;will create an integer stacks1.stack <char> s2;will create a character stacks2.stack <float> s3;will create a float number stacks3.
Suppose we create a stack
stack <float> s;of type integer and let us perform some basic operationspush - To insert an element in the stack we have the
void push(value)method. Suppose we want to push the integers 1, 2 & 3 in our stack.s.psuh(1);will push element 1 at the top of the stack.s.psuh(2);will push element 2 at the top of the stack.s.psuh(3);will push element 3 at the top of the stack.- So the stack after these operations will look like this:
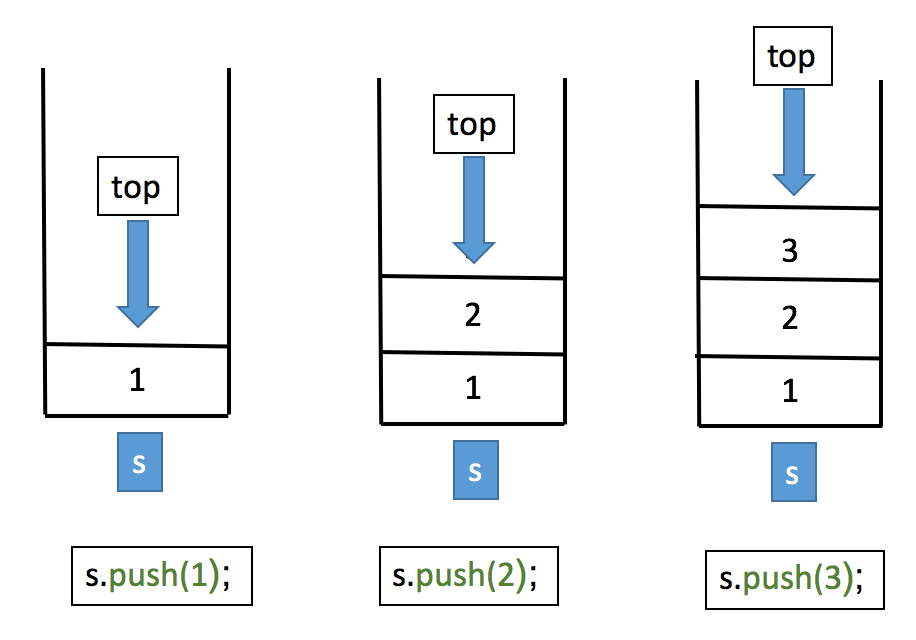
pop - To delete an element from the top of the stack we have the the
void pop()method. So if we want to remove the top most element from the stack we can simply dos.pop();top - to return the element at the top of the stack we have the
top()method.cout<<s.top();will produce the output 2.
empty - To check if the stack is empty or not we have the method
bool empty()which returns 0 if the stack is not empty and returns 1, if the stack is empty.- for stack s
cout<<s.empty();will produce the output as 0 because the stack is not empty.
- for stack s
size - The
size()method returns us the size of the stack that is the total number of elements in the stack.cout<<s.size();will give the output as 2.
# Source Code - C++
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
//function to display stack
void displayStack(stack<int> s)
{
int n = s.size();
for(int i=0; i<n;i++)
{
cout<<s.top()<<" ";
s.pop();
}
cout<<"\n";
}
// Main function
int main()
{
stack<int> s;
//push - inserting elements 1,2 & 3 in stack
s.push(1);
s.push(2);
s.push(3);
//display the stack
cout<<"Elements of Stack are : ";
displayStack(s);
//pop - deleting the element at top
s.pop();
cout<<"Stack after pop operation is : ";
displayStack(s);
//Display element at top
cout<<"Element at top is : "<<s.top()<<"\n";
//to check if queue is empty or not
cout<<"Stack is empty (1 - YES / 0 - NO) : "<<s.empty()<<"\n";
//Size of stack
cout<<"Size of stack is : "<<s.size()<<"\n";
return 0;
}
Time Complexity - Each operation is O(1)
Learn More
- Built in stack data structure in C++



